Circuit Safety Protection for Electric Irons SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions and Products
Overview
An Electric Iron is a household appliance that uses electrical heating to press clothes and fabrics, smoothing out wrinkles by softening fibers with heat or steam. Its features include a simple structure, ease of use, power ratings typically ranging from 300W to 1000W, and modern designs emphasizing energy efficiency, smart functionality, and safety (e.g., auto shut-off, temperature control systems). Electric irons are categorized into basic irons, temperature-adjustable irons, steam spray irons, and garment steamers. Temperature-adjustable irons allow automatic temperature regulation, while steam spray irons generate steam to moisten fabrics for enhanced ironing results.
Market data indicates that the global electric iron market was valued at approximately USD 17.3 billion in 2023. In China, retail sales reached about CNY 350 million in 2021, with an estimated increase to CNY 370 million in 2022. By 2025, the global market is expected to maintain steady growth, with some forecasts projecting further expansion by 2029. By 2030, the global steam iron market is anticipated to exceed USD 100 billion, driven by smart and premium products (data sourced from the web for reference only).


Why Electric Irons Require Circuit Protection Components
Electric irons are high-power appliances that generate high temperatures and currents during operation, posing risks such as electric shock, overload, short circuits, and overheating. Circuit protection components (e.g., fuses, thermal protectors, overload protectors, and leakage protectors) are critical for the following reasons:
Preventing Electric Shock:
Leakage protectors or grounding devices quickly disconnect power in case of electrical leakage, safeguarding users from electric shock.
Preventing Overload and Short Circuits:
Fuses or circuit breakers disconnect the circuit during excessive current (e.g., due to overload or short circuits), preventing wire overheating or fires.
Preventing Overheat Damage:
Thermal protectors (e.g., thermal cutoff switches or fuses) automatically cut power when internal temperatures exceed safe limits, preventing equipment damage or fires.
Enhancing Equipment Reliability:
By limiting abnormal currents or temperatures, protection components reduce damage to internal components (e.g., heating elements, circuit boards), extending the iron’s lifespan.
Compliance with Regulations:
Global and regional electrical safety standards mandate the use of circuit protection components to ensure product compliance and consumer safety.
International and Regional Standards
International Standards (IEC)
IEC 60335-1:
Requires electric irons to incorporate fuses, thermal protectors, or similar components to address overload, short-circuit, and overheating risks. The 6th edition includes additional requirements for software safety and battery-powered devices.
IEC 60335-2-3:
Specifies safety requirements for electric irons, mandating thermal fuses or temperature control switches to ensure safe power disconnection during high temperatures or abnormal operation (e.g., steam blockages). These standards are widely adopted and adapted into local mandatory regulations.
National/Regional Standards
China:
GB 4706.1 and GB 4706.2:
Mandatory standards requiring electric irons sold in China to pass CCC certification, verifying the use of necessary circuit protection components (e.g., fuses, thermal protectors). Non-compliant products are prohibited from sale.
United States:
UL 1008A and NFPA 70:
Mandate overload and overheat protection for electric irons. UL certification is required for market entry, with circuit protection components being a mandatory requirement.
European Union:
EN 60335-1 and EN 60335-2-3:
Mandatory standards requiring electric irons to incorporate protection components and obtain CE certification. The EMC Directive further requires circuit designs to minimize electromagnetic interference, indirectly involving protection components.
Australia/New Zealand:
AS/NZS 60335.1:
Requires electric irons to comply with safety standards, including circuit protection components, and bear the RCM mark.
Canada:
CSA C22.2 No. 60335-1:
Mandates protection components to prevent electrical and thermal risks, requiring CSA certification.
In most countries and regions, household appliances like electric irons must pass relevant safety certifications before market entry, with circuit protection components being a mandatory requirement. Non-compliant products may face sales bans, recalls, or legal penalties. Even in regions not strictly adopting IEC standards, manufacturers typically follow IEC 60335 series standards to meet global market compliance.
Electric irons require circuit protection components to ensure electrical safety, prevent fires and electric shocks, extend equipment lifespan, and comply with global and regional regulations. Standards such as IEC 60335-1, IEC 60335-2-3, GB 4706, UL, and EN mandate the use of fuses, thermal protectors, and other components, with specific requirements varying by market. Manufacturers must ensure products pass certifications (e.g., CCC, UL, CE) for legal market entry.
Why Electric Irons Use Disposable Thermal-Link (Thermal Fuse) for Circuit Protection
The Disposable Thermal-Link (Thermal Fuse) is a commonly used circuit protection component in electric irons to prevent safety incidents due to overheating. During operation, electric irons generate high temperatures, and failures in the temperature control system (e.g., thermostat malfunction) or improper use (e.g., unattended prolonged operation) can cause heating elements to overheat, leading to fires, equipment damage, or fabric scorching. The Thermal-Link serves as a final safety barrier, permanently disconnecting the circuit when temperatures exceed its rated threshold (typically 150°C to 240°C, depending on the model) by melting its internal thermal-sensitive material. This prevents further heating, protecting the device and user. Its advantages include rapid response, low cost, high reliability, and non-resettable design, ensuring faulty devices are not reused. Typically installed near heating elements and connected in series with the main power or heating circuit, the Thermal-Link works alongside thermostats and other protective devices to ensure compliance with international and national safety standards (e.g., IEC 60335, GB 4706.2). This simple, cost-effective, and efficient design is an essential part of electric iron safety systems.
Functions of Thermal-Link in Electric Irons
Overheat Protection:
When internal temperatures rise abnormally (e.g., due to thermostat failure or poor heat dissipation), the Thermal-Link fuses at its rated temperature, disconnecting power to prevent fires or component damage.
Preventing Electrical Failures:
In extreme conditions (e.g., short circuits or overloads causing localized overheating), the Thermal-Link rapidly interrupts current, protecting circuit boards and other critical components.
Enhancing Product Compliance:
Standards like IEC 60335-2-3 and GB 4706.2 mandate overheat protection devices. The Thermal-Link is a key component for meeting these standards and achieving certifications (e.g., CCC, UL, CE).
Installation of Thermal-Link in Electric Iron Circuits (For Reference)
Physical Location:
The Thermal-Link is typically placed near the heating element (e.g., soleplate or ceramic/metal heating tube) to accurately monitor temperature.
In steam irons, it may also be positioned near the steam generator or water tank heating area to prevent overheating in the steam system.
It is usually fixed on a metal bracket or secured with a dedicated clamp to ensure close contact with the heating element for efficient heat conduction.
Circuit Connection:
The Thermal-Link is connected in series with the main power circuit or heating element circuit, directly linked to the power input or heating element. When fused, it completely disconnects the circuit, stopping heating.
Its terminals are connected via welding, crimping, or dedicated connectors to ensure reliable electrical contact.
In some designs, the Thermal-Link is used alongside thermostats or other protective devices (e.g., thermistors) to form a multi-level protection system.
Installation Considerations:
The Thermal-Link’s rated operating temperature and current capacity must match the iron’s power and operating temperature (e.g., rated current typically 10A or 15A, with operating temperature selected based on design).
Ensure good thermal contact with the heat source during installation, while avoiding mechanical stress or external pressure that could cause malfunctions.
The Thermal-Link is non-resettable; if fused, it must be replaced by a professional technician.
SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions, Products
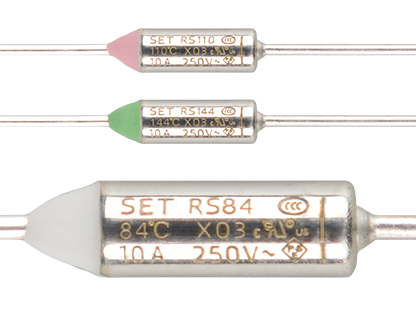
Protection Type: Over-Temperature Protection
Product Name:
Thermal-Link (Organic Type OTCO)
Series:
Axial Lead Type RS
Models: RS216, RS229, RS240, RS257, RS263 Learn more
Series:
Axial Lead Type RT
Models: RT216, RT229, RT240, RT257, RT263 Learn more
Why Choose SETsafe | SETfuse Thermal-Links
| Product Manufacturing: Fully Automated Intelligent Manufacturing.
| Complete Specifications: Maximum Rated Current Up to 30 A.
| Guaranteed Quality: Product Functionality, Performance, and Reliability are Verified.
15 More items than national standards: 30 reliability test items, Including Mechanical, Electrical, Temperature, Soldering, Environmental, and Life Tests.
41.67 Times Higher Than National Standards: Holding Temperature Test Duration is 1,000 hours (National Standard: 24 hours).
2.5 Times Higher Than National Standards: Operating Temperature Accuracy is ±2°C (National Standard: 0/-10°C).
| Multi-System Certifications: Learn more
| Environmentally Friendly Products: HSF (Compliant with RoHS 3.0, REACH, Halogen-Free) Learn more
| Diverse Industry Applications: Learn more
Company Expertise
| Over 25 years of professional design, manufacturing, and sales of circuit protection components, with products sold in over 40 countries and trusted by numerous Fortune 500 companies. Learn more
| Recognized as a National High-Tech Enterprise and a National Specialized, Refined, and Innovative Enterprise.
| EHS Compliance: Learn more
| Reliable Service
Professional support for pre-sales, in-sales, and after-sales with responses within 1 hour. Learn more
Other Circuit Protection Components Used in Electric Irons
Varistors
Function: Components like Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) absorb or suppress transient voltage spikes (e.g., from lightning or grid fluctuations), protecting electronic components (e.g., control circuit boards) from damage.
Summary
Circuit protection components for electric irons include Disposable Thermal-Links, thermostats, overload protectors, leakage protectors, thermistors, auto shut-off switches, surge protectors, and grounding systems. These components work together to address risks such as overheating, overcurrent, leakage, voltage fluctuations, and unattended operation, ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance with international and national standards (e.g., IEC 60335, GB 4706). Thermostats and auto shut-off switches provide dynamic protection, while Thermal-Links and leakage protectors serve as final safety barriers, collectively reducing risks of fire, electric shock, and equipment damage.
Why Choose SETsafe | SETfuse Thermal-Links
| Product Manufacturing: Fully Automated Intelligent Manufacturing.
| Complete Specifications: Maximum Rated Current Up to 30 A.
| Guaranteed Quality: Product Functionality, Performance, and Reliability are Verified.
15 More items than national standards: 30 reliability test items, Including Mechanical, Electrical, Temperature, Soldering, Environmental, and Life Tests.
41.67 Times Higher Than National Standards: Holding Temperature Test Duration is 1,000 hours (National Standard: 24 hours).
2.5 Times Higher Than National Standards: Operating Temperature Accuracy is ±2°C (National Standard: 0/-10°C).
| Multi-System Certifications: Learn more
| Environmentally Friendly Products: HSF (Compliant with RoHS 3.0, REACH, Halogen-Free) Learn more
| Diverse Industry Applications: Learn more
Company Expertise
| Over 25 years of professional design, manufacturing, and sales of circuit protection components. Our products are sold in over 40 countries, and many Fortune 500 companies choose SETsafe | SETfuse. Learn more
Guaranteed, Worry-Free Service
| Pre-sales, in-sales, and after-sales support with professional personnel (feedback within 1 hour) Learn more
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production

















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain