Outdoor Streetlight Overheating Safety Protection SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions and Products
Overview
Overheating in outdoor streetlights is a critical safety issue that can lead to functional failure, performance degradation, fires, or housing detachment.
Outdoor Streetlight Overheating Safety Protection
SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions and Products

Overheating in outdoor streetlights is a critical safety issue that can lead to functional failure, performance degradation, fires, or housing detachment. To address this, SETsafe | SETfuse offers Solutions and Products with Thermal-Link (Thermal Cutoff) technology.
Product:
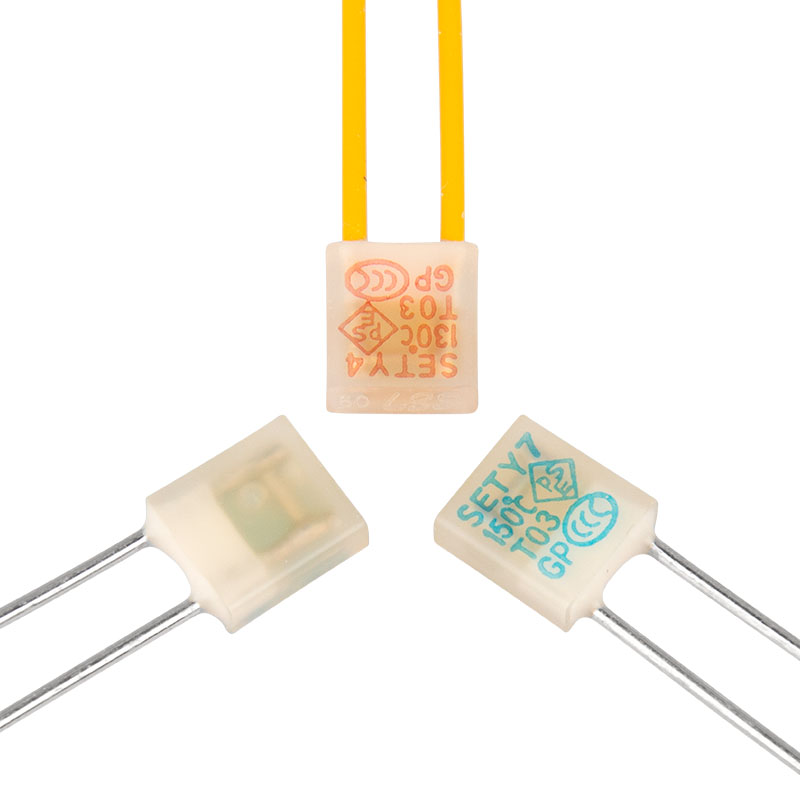
Thermal-Link Alloy Type (ATCO)
Specially designed for outdoor streetlight overheating protection:
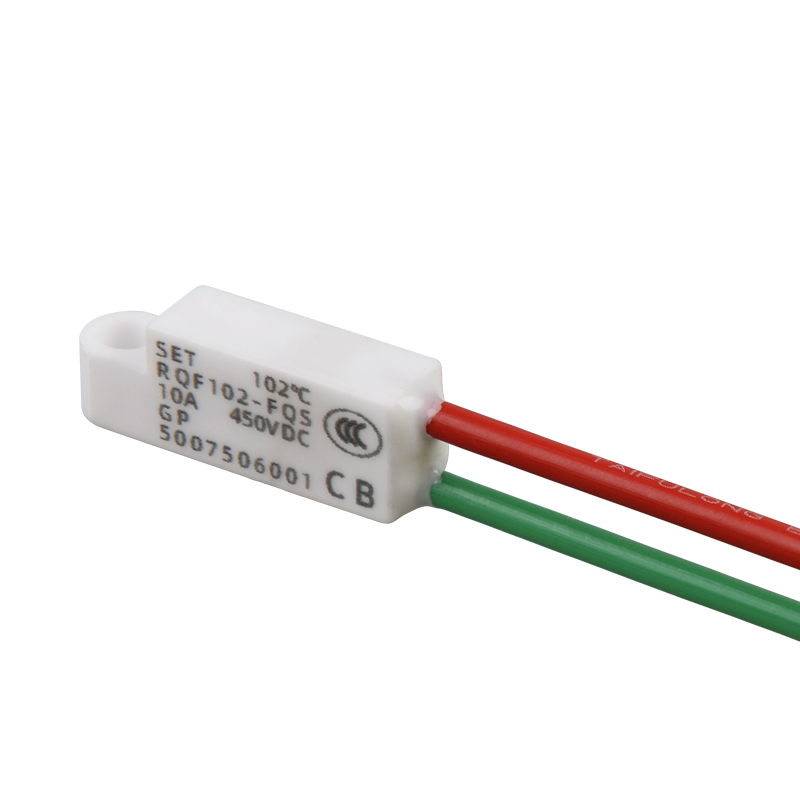

RQF Series Learn more
Y Series Learn more
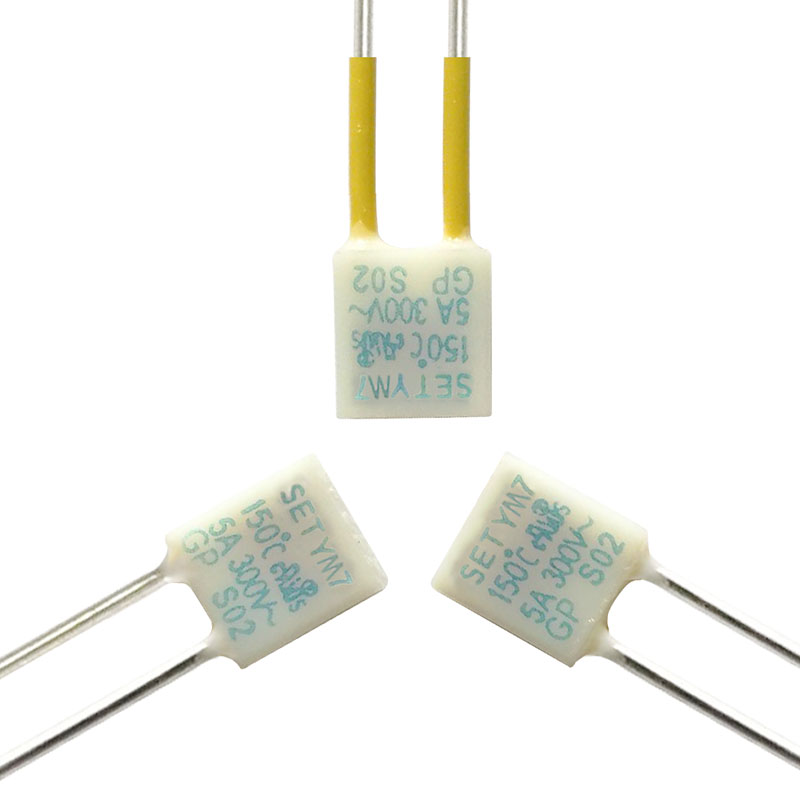
YM Series Learn more
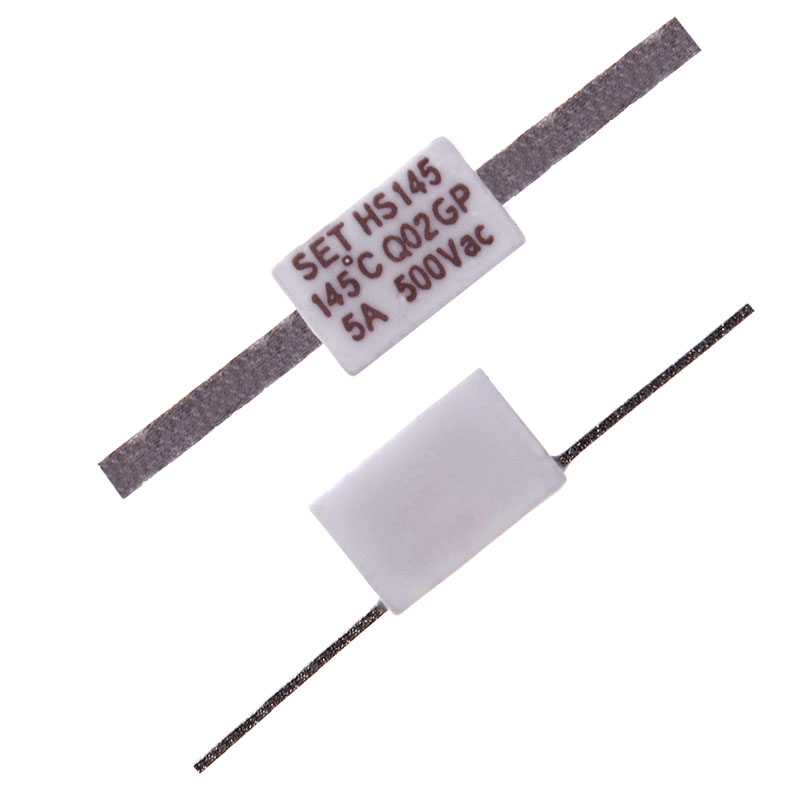
HS Series Learn more
Key Features:
Temperature-Sensitive Element.
Compact Size.
Precise Activation Temperature ±2°C.
One-Time, Non-Resettable Action.
RoHS and REACH Compliant.
Customizable Services.
Ratings: 10A, 450VDC, 86 - 187°C / 5A, 250VAC, 76 - 187°C / 5A, 690VAC, 130 - 150°C / 5A, 500VAC, 200VDC, 125 - 145°C.
Applications:
LED streetlights, solar streetlights, high-pressure sodium lamps, metal halide lamps, fluorescent streetlights, and wind-solar hybrid streetlights.
Protection Principle:
When the temperature of certain streetlight components reaches a dangerous level, the Thermal-Link (Thermal Cutoff) activates, permanently cutting off the circuit to prevent accidents.
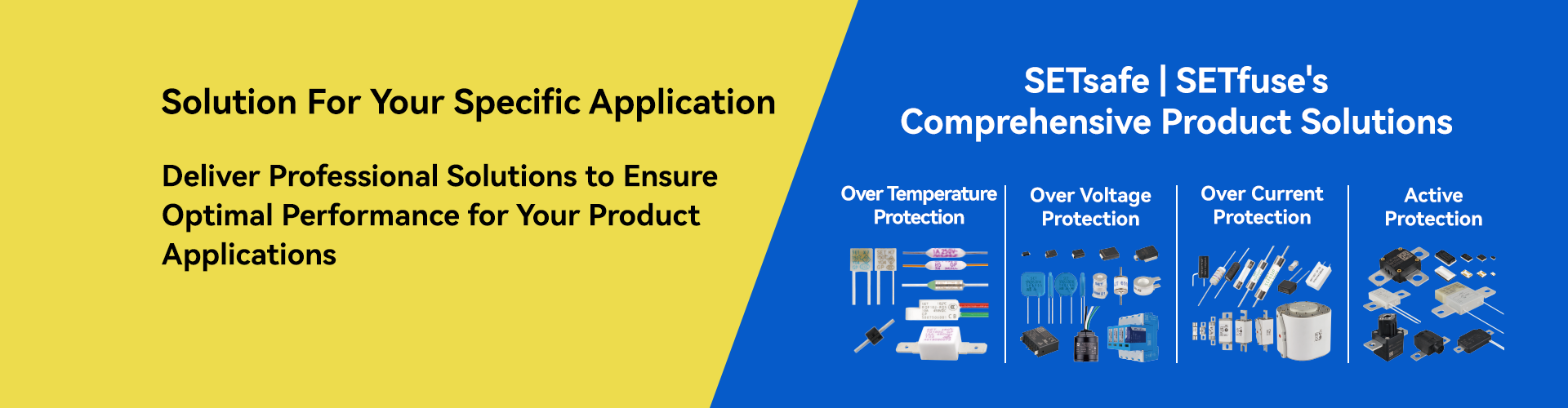
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production
Technical Article (For Reference Only)
Overheat Protection for Outdoor Street Lights
Areas Prone to Overheating in Street Lights
Overheating in outdoor street lights typically occurs in the following key areas:
LED Light Source Module:
LED chips generate significant heat during operation. Poor heat dissipation design can cause chip temperature to rise, leading to light degradation, reduced lifespan, or burnout.
Driver Power Supply:
The power module generates heat during voltage or current conversion. In high-load or low-efficiency designs, heat buildup can cause electrolytic capacitor aging or circuit failure.
Heat Sink:
Inadequate design or accumulation of dust and debris can hinder heat dissipation, raising the overall temperature of the lamp.
Housing and Connectors:
In high-temperature environments, the housing (especially if made of plastic or low-melting-point materials) may deform, crack, or detach, posing safety risks.
Circuit Board and Electronic Components:
Control circuits, sensors, or other components may experience solder joint loosening or failure under prolonged high temperatures.
Wiring Terminals:
Poor contact or excessive current through terminals can cause localized overheating, leading to burning or short circuits.
Issues Caused by High Ambient Temperatures
High ambient temperatures (e.g., during summer or in tropical regions) exacerbate the overall temperature rise of street lights, potentially causing:
Housing Detachment or Deformation:
Plastic or low-quality metal housings may soften, crack, or detach under prolonged heat, exposing internal circuits and increasing risks of electric shock or fire.
Reduced Light Source Performance:
LED efficiency and lifespan decrease with rising temperatures, potentially causing insufficient brightness or permanent damage.
Circuit Failures:
High temperatures accelerate component aging, increasing the risk of short or open circuits.
Safety Hazards: Overheating may lead to fires, electric shocks, or other accidents, especially in unattended outdoor environments.
Role of Overheat Protection Products
Overheat protection devices monitor temperature and cut off the main circuit when necessary to ensure safe operation. Common mechanisms include:
Temperature Sensors:
Thermistors (NTC/PTC) or thermocouples, installed in critical areas (e.g., LED module, power supply, or housing), monitor temperature in real time.
Over-Temperature Protection Circuit:
When the temperature exceeds a set threshold (e.g., 80°C or higher, depending on design), the circuit automatically cuts off power to prevent further heating.
Smart Control Systems:
Advanced street lights may include intelligent thermal management modules that reduce power (e.g., dimming LEDs) to lower heat generation instead of fully cutting off power.
Thermal Fuse:
As a last resort, a thermal fuse melts at dangerous temperatures, permanently cutting off the circuit to prevent accidents.
Scenarios Triggering Overheat Protection
Overheat protection is activated in the following cases:
High External Temperatures:
Such as during summer or in poorly ventilated areas (e.g., tunnels or enclosed fixtures).
Inadequate Internal Heat Dissipation:
Blocked heat sinks, failed fans, or design flaws cause heat buildup.
Circuit Abnormalities:
Power module failures, short circuits, or overloads lead to abnormal heat generation.
Prolonged High-Load Operation:
Street lights operating at high brightness for extended periods, with heat unable to dissipate in time.
Design Recommendations and Solutions
To reduce overheating risks and enhance protection, consider the following measures:
Optimize Heat Dissipation Design:
Use efficient heat-dissipating materials (e.g., aluminum alloy) and increase heat sink surface area to ensure rapid heat dissipation.
Select High-Temperature-Resistant Materials:
Use heat- and corrosion-resistant metals or engineering plastics for the housing to prevent deformation or detachment.
Install Temperature Sensors:
Deploy sensors in critical areas like LED modules, power supplies, and housings for real-time temperature monitoring.
Smart Thermal Control Systems:
Automatically reduce power or temporarily turn off some light sources when temperatures approach thresholds.
Regular Maintenance:
Clean dust and debris from heat sinks to maintain dissipation efficiency.
Redundant Protection:
Combine temperature sensors, thermal fuses, and smart controls for multi-layered overheat protection.
Conclusion
Overheating in outdoor street lights primarily occurs in LED light sources, driver power supplies, heat sinks, and housings. High ambient temperatures can lead to housing detachment, performance degradation, or safety incidents. Overheat protection products, through temperature monitoring and main circuit disconnection, effectively mitigate these risks. It is recommended to integrate efficient heat dissipation, high-temperature-resistant materials, and smart thermal control systems to enhance the safety and reliability of street lights.

















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain