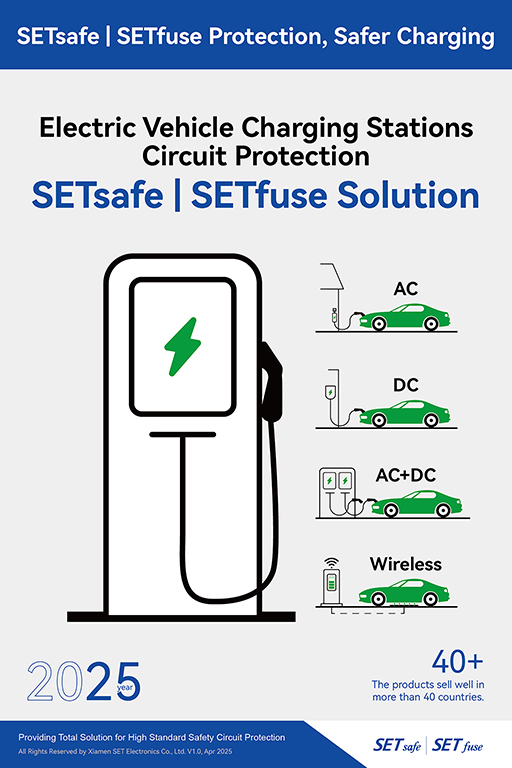
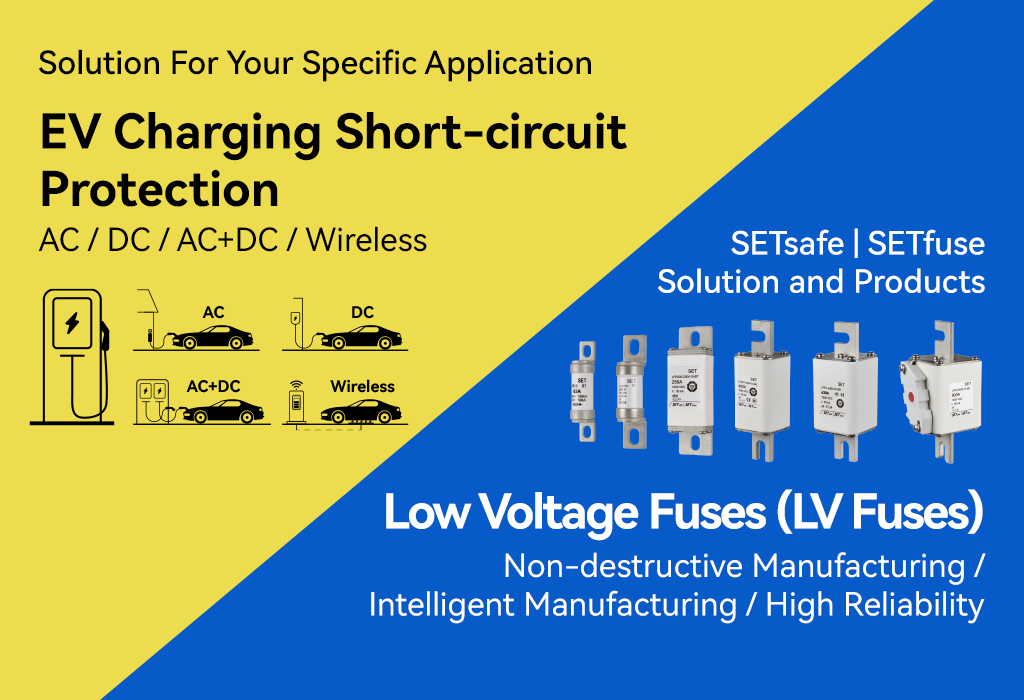
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Station Circuit Safety Protection SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions & Products
Overview
Adjust AC or DC grid power to certain calibrated voltage or current to provide power to the battery of electric vehicle, and also additionally provide power to the on-board electrical equipment. Charging systems include AC charging systems, DC charging, and wireless charging systems.
Why Is Circuit Safety Protection Necessary For Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations
Reason
Circuit safety protection for Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations is indispensable to ensure personnel safety, stable equipment operation, extended service life, and to prevent accidents such as fires. Common Risks (including but not limited to):
High Voltage and High Current Risks
Charging stations typically operate in environments with high voltages (220V AC or higher; DC fast charging can reach hundreds of volts) and high currents (tens to hundreds of amperes). Any circuit fault (e.g., short circuit, leakage) can lead to electric shock, equipment burnout, or fire.
Preventing Electric Shock and Personal Injury
Electrical leakage can cause users to experience electric shock when touching the charging station or vehicle. Residual Current Devices (RCDs) and grounding systems can quickly cut off power, protecting user safety.
Protecting Equipment and Batteries
Abnormal conditions such as overvoltage, undervoltage, and overcurrent can damage the charging station or the vehicle's battery. Circuit protection devices (e.g., overload circuit breakers, overvoltage protectors) can limit abnormal currents/voltages, extending equipment lifespan.
Preventing Fire and Overheating
Overload, short circuits, or poor contact in connectors can lead to line overheating, potentially causing fires. Temperature monitoring and overload protection can intervene promptly to prevent accidents.
Addressing Grid Fluctuations and Lightning Strikes
Grid voltage fluctuations or lightning strikes can cause instantaneous high voltage, damaging the charging station or vehicle's electronic system. Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) and overvoltage protection devices can effectively mitigate these external risks.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards:
National standards (e.g., China's GB/T 18487.1-2015) mandate that charging stations must be equipped with protection measures against leakage, overload, grounding, etc., to ensure legal and compliant operation.
Enhancing User Experience and System Reliability
Circuit protection can reduce issues such as charging interruptions and equipment failures, ensuring a stable charging process and improving user trust and experience.
Based on the reasons above, circuit safety protection is an essential design aspect of EV charging stations, aimed at preventing risks such as electric shock, fire, and equipment damage caused by high voltage/high current, while also meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring user safety and system reliability. Without these protective measures, charging stations could become safety hazards, hindering the promotion and use of electric vehicles.
SETsafe | SETfuse Solutions & Products
 EV Charging Stations Circuit Protection_SETfuse _ SETsafe Multi-Product Solution_V1.0_Apr 25, 2025.pdf
EV Charging Stations Circuit Protection_SETfuse _ SETsafe Multi-Product Solution_V1.0_Apr 25, 2025.pdf
Technical Article (For Reference)
Types of Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations
EV charging stations can be categorized based on charging method, power output, and installation scenarios. The main types are as follows:
By Charging Method
AC Charging Stations
Supply alternating current (AC), which is converted to direct current (DC) by the vehicle's onboard charger (OBC) to charge the battery.
DC Charging Stations
Provide direct current (DC), bypassing the vehicle's onboard charger to directly charge the battery.
By Installation Method
Wall-mounted charging stations
Pole-mounted charging stations
Portable charging stations
By Interface Standard
GB/T (Chinese Standard)
National standard in China, compatible with most domestic EVs.
European Standard (CCS2, Type 2)
Predominant in Europe, used by some imported vehicles.
North American Standard (CCS1, Tesla NACS)
Common in North America, frequently used by Tesla.
Japanese Standard (CHAdeMO)
Used in Japan, commonly for brands like Nissan.
Different standards may not be fully compatible; some charging stations support multiple interface standards.
By Application Scenario
Residential Charging Stations
Designed for individual users, typically providing slow charging for home use.
Public Charging Stations
Installed in public areas to meet diverse user needs, offering both fast and slow charging options.
Dedicated Charging Stations
Tailored for specific vehicles (e.g., buses, logistics vehicles), typically high-power DC charging.
Circuit Safety Protection Modes for EV Charging Stations
The circuit safety protection modes for EV charging stations are designed to ensure equipment safety, user safety, and the stability of the charging process. These protections combine hardware and software to mitigate potential electrical risks. Below are the common circuit safety protection modes, including overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, overtemperature protection, and other critical mechanisms:
Overvoltage Protection
Function:Prevents the grid or charging station output voltage from exceeding the safe range for the equipment or vehicle battery, avoiding damage to electronic components or the battery.
Typical Scenarios:Grid voltage fluctuations, lightning surges.
Overcurrent Protection
Function:Limits charging current to prevent it from exceeding the rated capacity of the charging station, cable, or vehicle battery, avoiding overheating or equipment damage.
Typical Scenarios:Excessive line load, poor contact in the charging connector causing abnormal current.
Overtemperature Protection
Function:Prevents damage or fire hazards due to overheating of the charging station, cable, or connector.
Typical Scenarios:Prolonged high-power charging, high ambient temperatures, poor heat dissipation.
Other Common Circuit Safety Protection Modes
Residual Current Protection (RCD)
Function:Detects leakage current (e.g., current flowing to ground through an unintended path) to prevent electric shock or equipment damage.
Typical Scenarios:Water ingress in the charging connector, damaged insulation in wiring.
Short Circuit Protection
Function:Prevents large currents caused by direct contact between positive and negative terminals or live and neutral lines, reducing fire and equipment damage risks.
Typical Scenarios: Aging wiring, internal short circuits in the charging connector.
Ground Fault Protection
Function:
Ensures proper grounding of the charging station and vehicle to prevent electric shock from leakage currents.
Typical Scenarios
Disconnected ground wire, improper installation.
Undervoltage Protection
Function
Prevents unstable operation of the charging station or vehicle battery due to excessively low grid voltage.
Typical Scenarios
Insufficient grid power supply, excessive voltage drop in the line.
Lightning Protection
Function
Protects the charging station from instantaneous high-voltage surges caused by lightning or grid disturbances.
Typical Scenarios
Outdoor charging stations operating during thunderstorms.
Communication Failure Protection
Function
Ensures stable communication between the charging station and the vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS), preventing charging anomalies due to protocol errors.
Typical Scenarios
Poor contact in the charging connector, incompatible protocols.
Overload Protection
Function
Prevents the charging station or circuit from operating in an overloaded state for extended periods.
Typical Scenarios
Multiple charging stations sharing the same grid capacity.
Summary
The circuit safety protection modes for EV charging stations include overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, overtemperature protection, residual current protection, short circuit protection, ground fault protection, undervoltage protection, lightning protection, communication failure protection, and overload protection. These mechanisms, implemented through hardware (e.g., circuit breakers, sensors) and software (e.g., BMS, charging station control systems), work collaboratively to mitigate risks such as electric shock, fire, and equipment damage, ensuring a safe and reliable charging process.
Partner with SETsafe | SETfuse to Transform Technical Challenges into Reliable Solutions
When you encounter technical challenges in selecting circuit protection components or designing system solutions, the professional engineering team at SETsafe | SETfuse is your trusted partner. Specializing in over-temperature, over-current, over-voltage, and active protection technologies, SETsafe | SETfuse offers comprehensive technical expertise and rapid response to meet your needs. Whether you require precise product parameter guidance or comprehensive system-level protection solutions, SETsafe | SETfuse delivers professional, practical, and efficient recommendations and support.
From initial design consultation and solution implementation to post-sales product assurance, we provide end-to-end collaboration, ensuring your project progresses seamlessly and reliably. For any inquiries or requirements, please contact us at: sales@SETfuse.com
Professional Circuit Protection, Supporting You from Concept to Production

















 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway
Lithium Battery Thermal Runaway Electric Power Tool
Electric Power Tool New Energy
New Energy PV Power Generation
PV Power Generation Wind Power Generation
Wind Power Generation Energy Storage Batteries
Energy Storage Batteries Energy Storage System (ESS)
Energy Storage System (ESS) Electric Vehicles
Electric Vehicles EV Charging Stations
EV Charging Stations Light Electric Vehicles
Light Electric Vehicles Home Appliances
Home Appliances Small Household Appliances
Small Household Appliances Large Home Appliance
Large Home Appliance Home Appliance Component
Home Appliance Component Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...)
Kitchen Appliances (Hotplates ...) Air Fryer
Air Fryer Coffee Machine
Coffee Machine Electric Iron
Electric Iron Smart Toilet
Smart Toilet Personal Digital Products
Personal Digital Products Lifestyle Appliances
Lifestyle Appliances Office Equipment
Office Equipment Walkie Talkie
Walkie Talkie Medical Analysis Instrument
Medical Analysis Instrument Medical Auxiliary Facility
Medical Auxiliary Facility Medical Instrument
Medical Instrument Lighting
Lighting Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Streetlight
Outdoor Streetlight Power Supply
Power Supply Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts)
Power Supply (Power < 20 Watts) HVDC in Data Centers
HVDC in Data Centers Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Battery Backup Unit (BBU)
Battery Backup Unit (BBU) Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Telecommunication
Telecommunication Automotive
Automotive Power Strip
Power Strip Surge Protection Power Strip
Surge Protection Power Strip Security & Protection
Security & Protection Tethered Drone
Tethered Drone Industrial Robot
Industrial Robot Humanoid Robot
Humanoid Robot Service Robot
Service Robot Specialty Robot
Specialty Robot Agricultural Irrigation Equipment
Agricultural Irrigation Equipment Smart Agricultural Greenhouse
Smart Agricultural Greenhouse Rail Transit Facility
Rail Transit Facility Rail-Vehicle
Rail-Vehicle Railway Power Supply
Railway Power Supply Fuel Dispenser
Fuel Dispenser Traffic Control System
Traffic Control System Traffic Signal Light
Traffic Signal Light Commercial Cleaning Equipment
Commercial Cleaning Equipment Delivery Locker (Drone)
Delivery Locker (Drone) Vending Machine
Vending Machine Lightning Protection Components
Lightning Protection Components HVAC Rooftop Systems
HVAC Rooftop Systems Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater
Outdoor Electric Wall Mounted Heater Flag Explain
Flag Explain