Xiamen SET Electronics Co., Ltd.
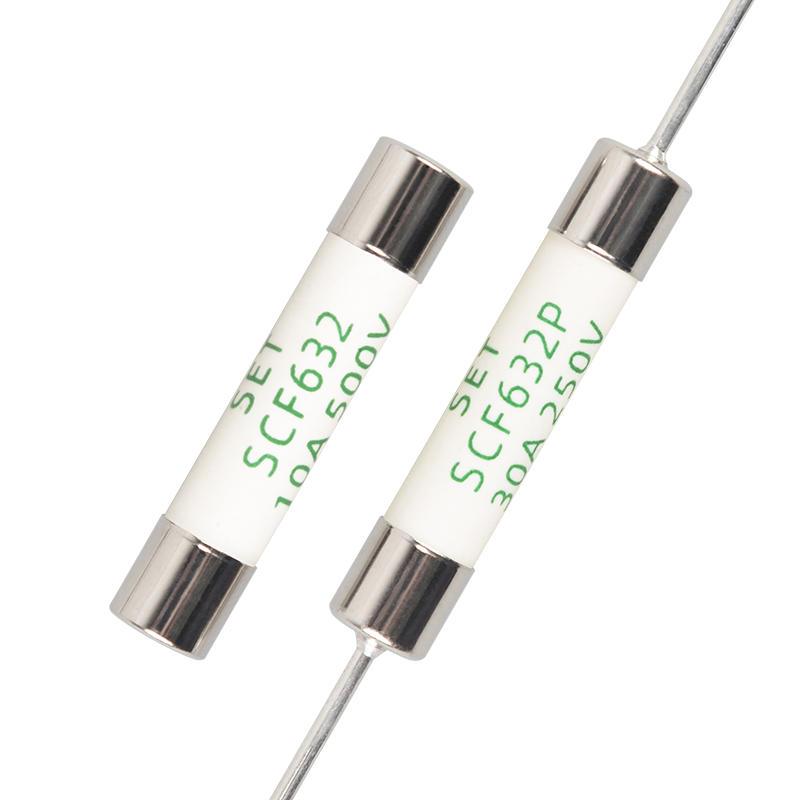
Miniature Fuses is an Over Current Protection device. Its resistance is very low. When the circuit works normally, it is equivalent to a wire, which can conduct the circuit continuously and stably. When the current fluctuates due to circuit instability or external interference, it should also be able to withstand a certain range of overload. Only when overload or short circuit happens, Miniature Fuses can blow fast to protect the circuit.
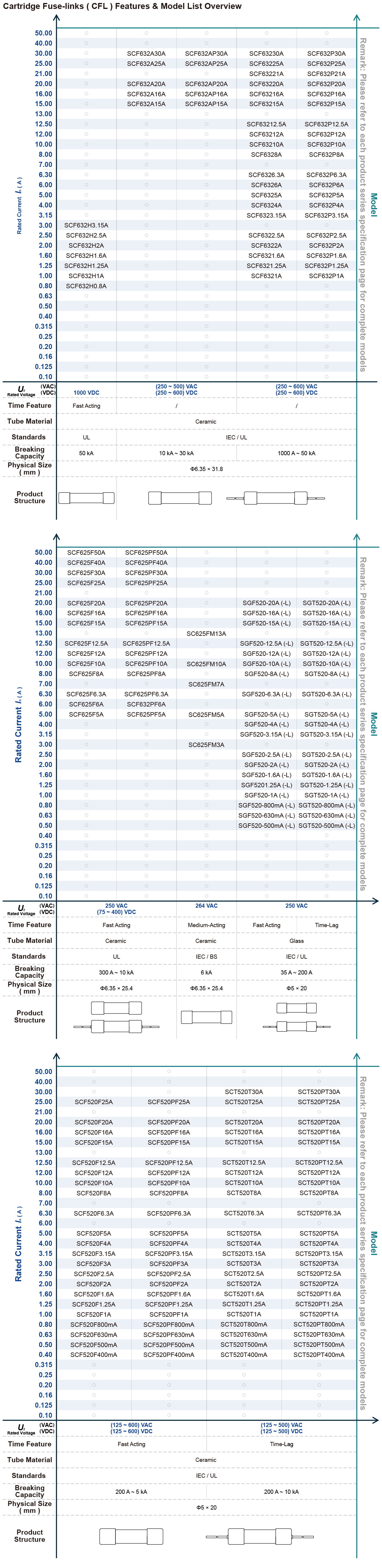
SETsafe | SETfuse Miniature Fuses is widely used in all kinds of electrical equipment. It has a variety of mounting modes, compact structure, reliable and stable performance. Technical parameters of SETsafe | SETfuse Miniature Fuses: Its rated current ranges from 0.1 A to 40 A, rated voltage ranges from 125 VAC to 500 VAC, and from 24 VDC to 600 VDC, complies with RoHS and REACH, and is approved by cURus, VDE, PSE, CCC, CQC, KC, TUV.
Fuse
A device, by the fusing of one or more of its specially designed and proportioned components, opens the circuit in which it is inserted by breaking the current when this exceeds a given value for a sufficient time.
— (IEC 60127)
Fast-Acting Fuse
A fuse which opens on overload and short circuits very quickly. This type of fuse is not designed to withstand temporary overload currents associated with some electrical load. UL listed or recognized fast acting fuses would typically open within 5 s when subjected to 200% to 250% of its rated current. IEC has two categories of fast acting fuses:
● F = Fast acting, opens on 10 times rated current within 0.001 s to 0.01 s.
● FF = Very fast acting, opens on 10 times rated current within less than 0.001 s.
— (UL 248)
Time-Lag Fuse
A fuse with a built-in delay that allows temporary and harmless inrush currents to pass without operating. In design, the breaking time under the condition of continuous overload and short-circuit current shall be: UL listed or recognized time delay fuses typically open in 2 minutes Max. when subjected to 200% to 250% of rated current. IEC has two categories of time delay fuses:
● T = Time-Lag, opens on 10 times rated current within 0.01 s to 0.3 s.
● TT = Long Time-Lag, opens on 10 times rated current within 0. 1 s to 1 s.
— (UL 248)
Rated Current
The rated current of a fuse identifies its current-carrying capacity based on a controllable set of test conditions. Each fuse is marked with its rated current, this rating can be identified with a numeric, alpha, or color code mark.
— (IEC 60127)
Rated Voltage
A Max. open circuit voltage in which a fuse can be used, yet safely interrupt an overcurrent. Exceeding the voltage rating of a fuse impairs its ability to clear an overload or short circuit safely.
— (IEC 60127)
RMS Current
The R.M.S. (root mean square) value of any periodic current is equal to the value of the direct current, which flowing through a resistance, produces the same heating effect in the resistance as the periodic current does.
— (IEC 60127)
Normal Operating Current
The normal operating current of a circuit is the level of current drawn (in RMS or dc amperes) after it has been energized and is operating under normal conditions. An operating current of 80% or less of rated current is recommended for operation at 25 °C to avoid nuisance openings. For example, a fuse with a Rated Current of 1 A is usually not recommended in circuits with normal operating currents of more than 800 mA. Further derating is required at elevated ambient Temp..
— (UL 248)
Ampere Squared Seconds I2t
The melting, arcing, or clearing integral of a fuse, termed I2t, is the thermal energy required to melt, arc, or clear a specific current. It can be expressed as melting I2t, arcing I2t or the sum of them, clearing I2t.
— (IEC 60127)
Overload
Can be classified as an overcurrent which exceeds the normal full load current of a circuit by 2 to 5 times its magnitude and stays within the normal current path.
— (UL 248)
Overcurrent
A condition which exists in an electrical circuit when the normal load current is exceeded. Overcurrent take on two separate characteristics-overloads and short circuits.
— (UL 248)
Short Circuit
An overcurrent that leaves the normal current path and greatly exceeds the normal full load current of the circuit by a factor of tens, hundreds, or thousands times.
— (UL 248)
Arcing Time
The amount of time from the instant the fuse link has melted until the overcurrent is interrupted, or cleared.
— (IEC 60127)
Clearing Time
The total time between the beginning of the overcurrent and the final opening of the circuit at rated voltage by an overcurrent protective device. Clearing time is the total of the melting time and the arcing time.
— (IEC 60127)
Breaking Capacity Of A Fuse-link
Value (r.m.s. for AC) of prospective current that a fuse-link is capable of breaking at a stated voltage under prescribed conditions of use and behaviour.
— (IEC 60127)
Holder, Clip, Board Mount, PCB Mount, Surface Mount

SETsafe | SETfuse Quality Policy
Provide Industry-Leading Products
Raw-materials Supplier
Select critical raw materials: Must be from a manufacturer with quality management system (ISO9001, IATF16949) certification.
Annual or Quarterly Audits.
IQC (Incoming Quality Check)
AQL(MIL-STD-105E), Dimensions, Function, Visual Inspection, RoHS & REACH Test.
Document
Formulate corresponding incoming inspection specifications (01-QA-06-xxx) for each key material according to design data such as material technical indicators.
Testing Equipment and Tools
Projector, Tool Microscope, Salt Spray Tester, Universal Material Testing Machine, Spectrum Analyzer, etc.

Manufacturing Process
Online Inspection and Testing (Function 100% Automatic Testing).
Document
Process Flow Chart.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
Quality Control Flow Chart (QCFC).
Standard Inspection Procedure (SIP).
Work Instruction (WI).
Online Testing and Inspection
Resistance test system (100% Automatic Testing).
100% Visual inspection, CCD, SMD Product 100% AI system.
etc.

IPQC (In Process Quality Control) Inspection
AQL(MIL-STD-105E), Dimensions Inspection, Function Test, Visual Inspection.
FQC ( Final Quality Control)
AQL(MIL-STD-105E), Dimensions Inspection, Function Test, Visual Inspection, RoHS & REACH Test.
Reliability Test
Test specification (01-TE-01-3001-xxx).
Including 23 items of appearance requirements, Electrical Performance, Mechanical Performance, Soldering Performance, Environmental Test and Life Test. e.g.
Voltage Drop Test.
Time-Current Characteristic Test.
Breaking Capacity Test.
High Temperature Test.
Cold Resistance Test.
Temperature Rise Test.
Surge Test.
etc.
OQC (Outgoing Quality Control)
AQL(MIL-STD-105E), Packaging, Labeling, Quantity Inspection.
Agency
Agency (Safety Certificate) Annual, Quarterly Audits.
Management System
ISO9001, (TUV approved and issued certificate).
ISO14001, ISO45001, etc.
Click to view the certificate
Environmental
RoHS & REACH Compliant.
SETsafe | SETfuse

Inspection
Cold Resistance Test
a. Applied current shall be less than 10% of rated current, at ambient Temp. of (23±2) °C.
b. (4-Wire) Resistance Measurement.
Usage
a. Do not touch the fuse body or lead wire when power on, avoiding scald or electric shock.
b. Air pressure is 80 kPa to 106 kPa. These values represent an altitude of +2000 m to -500 m, respectively.
Replacement
For safety reasons, the Fuse is the non-resettable product, please ensure that the alternative Fuse is the same type when replace it.
Storage
Please store the fuse in the environment without high temperature, high humidity or corrosive gas, to avoid reducing the
solderability of the lead wire. Please use them up within 1 year after receiving the goods.
Installation
Mechanical stress
Do not apply mechanical stress to the fuse body during or after the installation.
Wave soldering Parameters (For Reference Only)
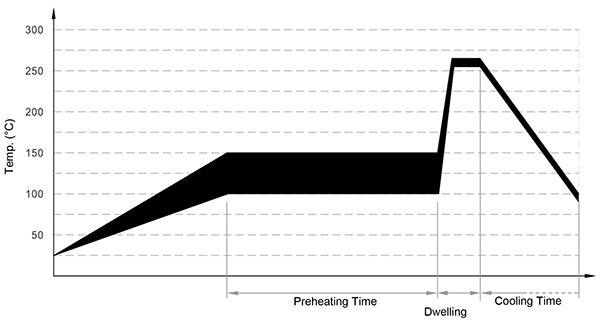
Recommended Hand-Soldering Parameters
Solder Iron Temp.: (350 ± 5) °C
Heating Time: 5 seconds Max.
Learn more
Click "Learn more" to jump to the Product Catalog (Datasheet) download page to download and read.
For more information, please contact SETsafe | SETfuse: sales@SETfuse.com.

















 Over Temperature Protection(87)
Over Temperature Protection(87)




 Over Voltage Protection(243)
Over Voltage Protection(243)








































 Over Current Protection(63)
Over Current Protection(63)
























 Active Protection(19)
Active Protection(19)






 Accessories(3)
Accessories(3)